Hip Resurfacing
Patients with advanced arthritis of the hip may be candidates for either traditional total hip replacement (arthroplasty) or hip resurfacing arthroplasty.
Each of these procedures is a type of hip replacement,
but there are important differences.. In hip replacement surgery the worn bone and cartilage of the hip joint is removed and replaced with prosthetic components.
What is Hip Resurfacing?
Hip resurfacing is a bone-conserving alternative to total hip replacement primarily used for younger,
active patients suffering from hip arthritis or hip damage. Unlike total hip replacement, hip resurfacing
preserves more of the patient's natural bone structure using a bone sparing prosthetic implant with
excellent wear, impact resistance, and reduced dislocation rate. 1
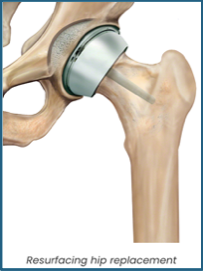
What is the difference between Hip Resurfacing and Total Hip Replacement?
In hip resurfacing, the femoral head is not removed, but is instead trimmed and capped with a smooth metal covering. The damaged bone and cartilage within the socket are removed and replaced with a metal shell. No stem implant into the femur is required.
In a traditional Total Hip Replacement, the head of the femur (femoral head) and the damaged socket (acetabulum) are both removed and replaced with metal, plastic, or ceramic components. A stem implant is placed into the centre of the upper femur.
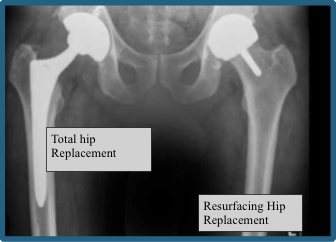
Total Hip Replacement vs Hip Resurfacing
What are the Advantages of Hip Resurfacing?
Hip resurfacing offers several advantages, particularly for younger and more active patients. Significant benefits include:
- Bone preservation: the procedure maintains more of the patient's natural bone compared to a total hip replacement. This is crucial for those who might need another hip procedure in the future (e.g young patients), as it leaves more bone intact for potential future surgery. 2
- Lower risk of dislocation: the larger size of the resurfaced femoral head, more closely matches the natural anatomy of the hip joint decreasing the dislocation risk. 3
- More natural joint movement:
because the femoral neck is preserved during hip resurfacing, a hip that feels more like the natural joint and has more natural movements can be obtained allowing patients to return to a wider variety of sports and leisure activities.
4
- Easier to revise: where revision surgery becomes necessary, it is generally easier to perform a total hip replacement following hip resurfacing than revising an existing total hip replacement.
5
- Superior durability:
hip resurfacing can be superior in durability, especially for young and active individuals, as the metal-on-metal components used in the procedure are highly impact and wear resistant and can withstand high levels of activity including running and impact sports.
6
- Associated with better function and higher activity levels post-surgery: likely due to the more natural hip biomechanics preserved with resurfacing patient's report improved functional outcomes compared to total hip replacement.
What are the Disadvantages of Hip Resurfacing?
- Hip resurfacing is
not suitable for everyone: patients with poor bone quality or significant deformities of the femoral head or small femoral heads may not be good candidates for this procedure.
- Risk of femoral neck fractures: The preservation of the femoral neck in hip resurfacing also means that there is a risk of femoral neck fractures post-surgery.
- Potential for
metal-ion adverse reaction: one of the main reasons for concern is the potential for metal-ion release from the metal-on-metal (MoM) implant components, which can lead to local tissue reactions and systemic effects in some patients. This issue is particularly significant in individuals with metal allergies or sensitivities. While MoM implants have a very low wear and impact rate. MoM hip implants that involve a metal ball and socket can generate microscopic wear particles through normal use. These particles can release metal ions, primarily cobalt and chromium causing a local allergic reaction. The incidence of these reactions is less than 1% for modern hip resurfacing.
7
- More complex surgical procedure: compared to total hip replacement, hip resurfacing is a more complex surgical procedure and requires a higher level of surgical expertise and experience.
We acknowledge that historically, there have been catastrophic failures of various types of metal-on-metal hip replacements and hip resurfacing that underwent global product recalls. Some implants required many patients to have earlier than expected revision surgery. Understand that these implants have never been used by Dr Agolley and are currently not available in Australia. Approved resurfacing implants for use in Australia (Birmingham and Adept) have excellent survivorship rates in the Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry (AOANJRR). 8. Ceramic on ceramic and metal poly implants for hip resurfacing are still in the trial phase and the benefits of these implants may resolve some of the current contraindications to hip resurfacing. We hope to see these bearing offerings on the wider Australian market soon.
| Who is Hip Resurfacing Suitable for? | Who is Hip resurfacing not be suitable for? |
|---|---|
| Patients with large bone (typically men) who are fit, active and under 65 years of age, with good bone quality. | Patients with poor bone quality (osteoporosis). |
| Active individuals who wish to maintain high levels of physical activity. | Individuals with severe bone deformities. |
| Patients with small femoral heads | |
| Patients with kidney impairment due to the risk of metal-ion release. | |
| Those with metal allergies or sensitivities. | |
| Most women (due to both their smaller skeletal frame and a higher sensitivity to metal-ions) |
What about Ceramic on Ceramic (CoC) Hip resurfacing?
Ceramic hip resurfacing uses ceramic materials instead of metal (cobalt alloy) to resurface the hip joint. The
ReCerf
ceramic implant, produced by MatOrtho, is based on the successful
Adept metal version, the key difference being the material. While this technique shows promise due to its low wear rates and biocompatibility, it is still in the clinical trial phase and not widely available in Australia.
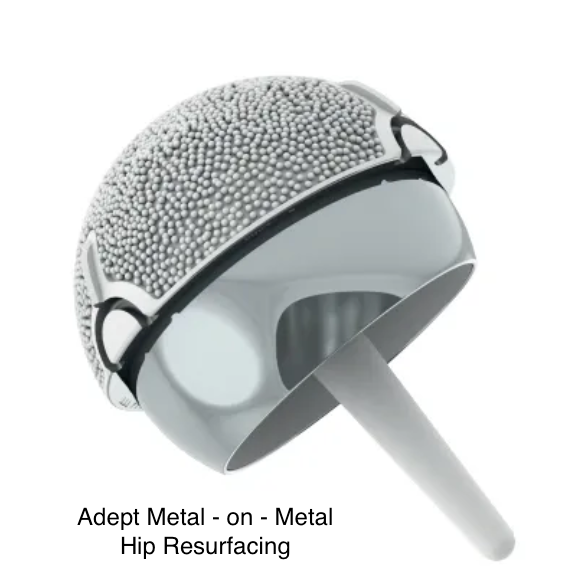

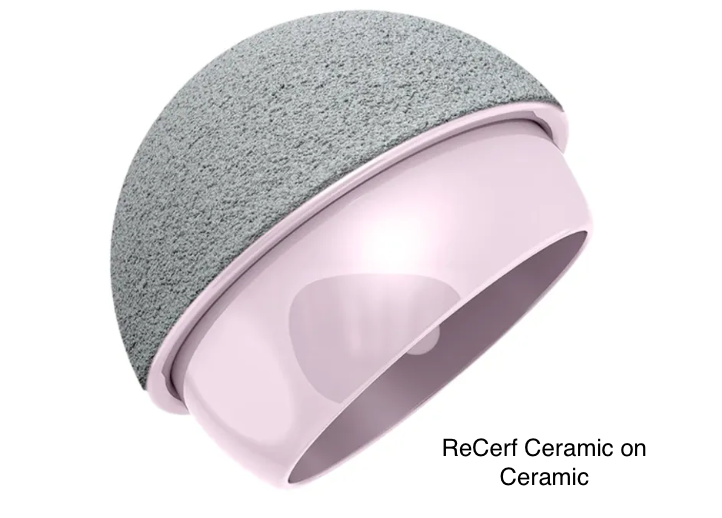
Although metal hip resurfacing yields excellent outcomes, it isn’t suitable for everyone, particularly those with smaller hip joints, such as women, who are at higher risk for metal allergies. Ceramic implants avoid cobalt-related allergic reactions, which occur in about 0.5% of metal resurfacing cases, making ceramic resurfacing a good alternative for patients who are unsuitable for metal implants. For patients who meet the criteria for metal resurfacing, the metal option is still recommended, as it has a proven track record with long term clinical data.
Ceramic hip resurfacing is relatively new, and long-term outcomes are not yet fully documented. Although Biolox Delta ceramic, used in the ReCerf implant, has a strong record in total hip replacement, its use in resurfacing is still being evaluated. The first ReCerf procedure was performed in 2018, with current results being favourable (AOANJRR Hip, knee and shoulder Arthroplasty: 2024 Annual report). Typically, however 10 years of follow-up data are needed to fully assess an implant’s performance.
Ceramic hip resurfacing offers a promising alternative for patients with hip arthritis, especially those who cannot use metal implants. However, more clinical data is needed before it becomes widely available in Australia.
What are the Long-term Outcomes for Hip resurfacing?
Longevity:
Hip resurfacing implants can last 15-20 years or longer in suitable patients.
Activity level:
Hip resurfacing has a high success rate improving pain and patient function with many patients returning to high-impact activities
Does Dr Agolley Perform Hip Resurfacing?
Yes. Dr Agolley has a specialty interest and training in all areas of hip surgery including Hip preservation surgery, Hip Arthroscopy (keyhole surgery), Hip Resurfacing, Total Hip Replacement, Robotic assisted Hip Replacement and revision Total Hip Replacement.
Patient Centred Care
Many people with moderate hip arthritis may not require surgical intervention. Dr Agolley will recommend treatment based on a detailed clinical assessment and patient discussion, ensuring you understand the potential outcomes and complications of all interventions including those associated with hip resurfacing. There are many options to consider before hip resurfacing is recommended as a surgical treatment option for you. For any questions or if you would like to discuss your condition, please schedule a consultation. Our team is here to support and provide you with the highest quality care.
Comparison of Total Hip Replacement and Hip Resurfacing
| Traditional Total Hip Replacement | Hip Resurfacing | |
|---|---|---|
| Procedure | Complete Replacement of the hip joint | Resurfacing of the femoral head with a metal cap and inserting a metal socket |
| Bone Preservation | Removes more bone from the femur | Preserves more of the patient’s natural bone |
| Ideal Candidate | Older less active patients typically over 65yrs with significant arthritis | Younger more active patients typically less than 65yrs with good bone quality |
| Implant Longevity | High longevity with implants lasting 20+ years | Potentially longer lasting for younger, active patients due to bone preservation |
| Recovery Time | Several months | Associated with faster recovery time due to less invasive surgery |
| Activity level post -surgery | May have restrictions on high impact activities | Higher likelihood of returning to higher impact activities |
| Advantages | -Broader range of patient suitability -High success rate -Suitable for most patients with severe hip arthritis -Improved Ability to correct significant leg length discrepancy | -High success rate -Revision surgery simplified -Lower incidence of dislocation -Wear and impact resistant better suited for high impact sports and running |
| Disadvantages | Higher dislocation rate Removes more bone from femur Revision surgery more difficult due to bone removal | Not suitable for all patients including patients with metal sensitivity Limited ability to correct significant leg length discrepancy |
| Surgical complexity | Well established procedure with a high success rate Suited to Direct Anterior | Fewer surgeons are specialised in this procedure. Best suited to Posterior Approach |
References
1 Dhawan R, Young DA, Van Eemeren A, Shimmin A. Birmingham Hip Resurfacing at 20 years. Bone Joint J. 2023
Sep 1;105-B(9):946-952. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.105B9.BJJ-2022-0713.R2. PMID: 37652450.
2 Ramkumar PN, Shaikh HJF, Woo JJ, Haeberle HS, Pang M, Brooks PJ. Hip resurfacing arthroplasty as an alternative to total hip arthroplasty in patients aged under 40 years. Bone Jt Open. 2023 Jun 1;4(6):408-415. doi: 10.1302/2633-1462.46.BJO-2023-0015.R1. PMID: 37257853; PMCID: PMC10232079.
3 NJR 19th Annual Report, 2022: Surgical data to 31 December 2021. njrreports.org.uk
4 satisfaction after hip resurfacing arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013 Feb;471(2):444-53. doi: 10.1007/s11999-012-2645-4. PMID: 23076552; PMCID: PMC3549167.
Oxblom, A., Hedlund, H., Nemes, S., Brismar, H., Felländer-Tsai, L., & Rolfson, O. (2019). Patient-reported outcomes in hip resurfacing versus conventional total hip arthroplasty: a register-based matched cohort study of 726 patients. Acta Orthopaedica, 90(4), 318–323. https://doi.org/10.1080/17453674.2019.1604343
5 Ramkumar PN, Shaikh HJF, Woo JJ, Haeberle HS, Pang M, Brooks PJ. Hip resurfacing arthroplasty as an alternative to total hip arthroplasty in patients aged under 40 years. Bone Jt Open. 2023 Jun 1;4(6):408-415. doi: 10.1302/2633-1462.46.BJO-2023-0015.R1. PMID: 37257853; PMCID: PMC10232079.
6 Dhawan R, Young DA, Van Eemeren A, Shimmin A. Birmingham Hip Resurfacing at 20 years. Bone Joint J. 2023 Sep 1;105-B(9):946-952. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.105B9.BJJ-2022-0713.R2. PMID: 37652450.
7 Girard J, Miletic B, Deny A, Migaud H and Fouilleron N. Can Patients return to high-impact physical activities after hip resurfacing? A prospective study. International Orthopaedics (SICOT), 2013, 37: 1019-1024.
8 AOANJRR. Mortality of Primary Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: Supplementary Report, 2022 Annual Report, AOA, Adelaide; 2022: 1-14.

